Materials Guide
by
IDEX Health & Science
Select the material(s) of your choice, from the listing below, to view properties and solvent compatibility.
Access PDF Version of the Materials Guide
316 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel is one of the most popular manufacturing materials currently being used in chromatography applications. It offers tremendous physical strength as well as the best chemical resistance of all of the 300-series stainless steels. Because of the metallic nature of this material, it is best to compare the chemical being used with a database listing to determine if any interaction is suspected.
| Temperature Range | up to 250 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 1 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation; ethylene oxide; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Acrylic
Acrylic

Acrylic is a widely used polymer that is primarily known for its transparency and high strength.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 748 cc / 100 in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide, thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Delrin® (Polyoxymethylene)
Delrin®

Delrin® is a rugged polymer that serves as an excellent choice for long-term mechanical stability for products such as fittings and threaded adapters. It is important to note that Delrin, while being strong mechanically, cannot tolerate to be in the presence of acidic or basic solutions for long periods of time, as the polymer will degrade. It is best to use Delrin with neutral pH aqueous solutions or organic solutions for guaranteed best performance.
| Temperature Range | up to 60 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 6 to 8 |
| Sterilization Techniques | |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Delrin Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.42 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min | 1 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | ||
| Moisture Absorption at Equilibrium | 50% RH | ASTM D570 | % | 0.22 |
| Water Absorption at Saturation | Immersion | ASTM D570/ ISO 62 | % | 0.9 |
| Hardness, Rockwell M | ASTM D785 | – | 94 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 120 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 69(10,008) |
| Elongation | break | ASTM D638 | % | 75 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | GPa | ASTM D638 | 406 ksi | 2.8 |
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | ASTM D790 | 421 ksi | 2.9 |
| Flexural YieldStrength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 99 | |
| Izod Impact Strength | J/cm | ASTM D256 | 2.3ft-lb/in | 1.23 |
| Unnotched, J/cm no break | ASTM D256 | 1,871ft-lb/in | 999 | |
| Izod Impact Low Temp | Notched, J/cm at -40 °C | ASTM D256 | 1.8ft-lb/in | 0.96 |
| Tensile Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | ASTM D1822 | 170ft-lb/in2 | 358 |
| Compressive Yield Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 124(17,985) | |
| Shear Strength | ASTM D732 | MPa(psi) | 66(9,573) | |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, 1E+6 cycles | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Poissons Ratio | – | 0.35 | ||
| Coefficient of Friction | Dynamic vs. carbon steel, 50mm/s (2in/s) | 2MPa | 0.35 | |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C linear 100 °C | µm/m- °C µm/m- °C | 60µin/in- °F 83µin/in- °F | 122 149 |
| Deflection Temperature | at 0.46 MPa, °C at 1.8 MPa, °C | ASTM D648 ASTM D648 | 336 °F 257 °F | 169 125 |
| Melting Point °C | °C | ASTM D3418 | 347 °F | 175 |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Deflection Temp at 1.8 MPa | – | 257 °F | 125 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m-K | – | 2.8BTU-in/hr-ft2- °F | 0.4 |
| Flammability, UL94 | (5=V-0;4=V-1;3=V-2;1=HB) | UL94 | HB | 1(HB) |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 1E+15 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 3.7 |
| Dielectric Strength, kV/mm | 2.3mm (90 mils); Short Time | ASTM D149 | 500 kV/in | 19.7 |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 0.005 |
| Arc Resistance | ASTM D495 | sec | 220 |
FEP
FEP

FEP is a nice, melt-processed alternative to PTFE. FEP exhibits many similar properties to the more familiar PTFE, while being melt-processable, allowing for a lower gas permeability and improved optical clarity.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 748cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide, thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
FEP Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. | ASTM D570 | % | 0.004 |
| Weather and Chemical Resistance | – | – | outstanding | |
| Limiting Oxygen Index | ASTM D2863 | % | 93 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D2116 | MPa(psi) | 23(3,400) |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D792 | – | 2.13-2.17 | |
| Ultimate Elongation | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D2116 | % | 300 |
| Flexural Modulus | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 586(90,000) |
| Impact Strength | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D256 | J/m(ft-lb/in) | 586(90,000) |
| Hardness Durometer | ASTM D2240 | Shore D | 56 | |
| Comprehensive Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 21(3,100) | |
| Linear Coefficient of Expansion | 0-100 °C 32-212 °F | – – | mm/mm/ °C in/in/ °F | 13.5 x 10-5 7.5 x 10-5 |
| Thermal | Test Method | Units | Typical Value | |
| Nominal Melting Point | DTA-E168 | °C (°F) | 255-265(491-510) | |
| Flow Rate | ASTM D2116 | g/10 min | 7 | |
| Upper Service Temperature | UL746 | °C (°F) | 204(400) | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | 0.25 mm (0.010 in) | ASTM D149 | kV/mm (V/mil) | 80(2,000) |
| Dielectric Constant | 1 MHz, 23 °C(73 °F) | ASTM D1531 | – | 2.02 |
| Dissipation Factor | 1 MHz, 23 °C(73 °F) | ASTM D1531 | – | 0.0007 |
| Volume Resistivity | ASTM D257 | Tohm-m (ohm-cm) | >103 (1017) | |
| Arc Resistance | ASTM D495 | seconds | No Track |
Halar®
Halar®

Halar® (ETCFE) is a chemical relative to PTFE, sharing its excellent chemical resistance properties. There are only a few chemicals that react with Halar, including tetrahydrofuran (THF) and pyridine. Several chemicals will have reduced resistance with elevated temperatures, please see the chemical compatibility section for more information.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | N/A |
| Oxygen Permeability | 25 cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 1 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Gamma irradiation; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Halar Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.68 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min | 2 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | 0.10 | |
| Moisture Absorption at Equilibrium | 50% RH | ASTM D570 | % | <0.01 |
| Hardness, Shore D | ASTM D2240 | – | 75 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 90 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Yield | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 30(4,300) |
| Tensile Strength | Break | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 54(7,800) |
| Elongation | Yield | ASTM D638 | % | 5 |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 250 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ASTM D638 | GPa(ksi) | 1.6(240) | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | GPa(ksi) | 1.7(245) | |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 47(6,800) | |
| Izod Impact Strength | ASTM D256 | J/cm | No break | |
| Izod Impact Low Temp | Notched, at -40 °C | ASTM D256 | J/m(ftlb/in) | 207(2.0) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Dynamic vs. carbon steel, 50mm/s (2in/s) | ASTM D1894 | 0.2 | |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C | µin/in- °F | 56 | |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8 MPa | ASTM D648 | °C(°F) | 63(145) |
| Melting Point °C | ASTM D3418 | °C(°F) | 240(464) | |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Deflection Temp at 1.8 MPa | – | °C(°F) | 148(300) |
| Thermal Conductivity | – | (W/m-K)BTU-in/hr-ft2- °F | 1.05(1.09) | |
| Flammability | UL-94 @3.1 mm | UL94 | Class | V-0 |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 5.5E+16 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 2.57 |
| Dielectric Strength, kV/mm | 3.2mm (90 mils); Short Time | ASTM D149 | Volts/mil(kV/mm) | 350(14) |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 0.013 |
| Arc Resistance | ASTM D495 | sec | 50 |
PCTFE (PolyChloroTriFluoroEthylene)
PCTFE (PolyChloroTriFluoroEthylene)

Chemicals which interact with PCTFE polymer are not pH dependent; rather, interaction is more determined by other physical properties of the chemical(s) in question. In general, only THF and a few halogenated solvents will react with this polymer. DMSO.
| Temperature Range | up to 80 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 12cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation; ethylene oxide; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
PCTFE (PolyChloroTriFluoroEthylene) Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 Hour | ASTM D570 | % | <0.01 |
| Density | ASTM D792 ASTM D792 | lb/in3 lb/in3 | 0.076 2.1 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D638 | psi | 5,700 | |
| Tensile Modulus | ASTM D638 | psi | 207,000 | |
| Tensile Elongation | at break | ASTM D638 | % | 150 |
| Flexural Strength | ASTM D790 | psi | 8,500 | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | psi | 180,000 | |
| Compressive Strength | ASTM D695 | psi | 5,500 | |
| Compressive Modulus | ASTM D696 | psi | 180,000 | |
| Hardness | Shore D | ASTM D785 | – | D75-80 |
| IZOD | Notched Impact | PTM55010 | ft-lb/in | 5 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Melting Point °C | ASTM D3418 | °C (°F) | 212(415) | |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | ASTM D696 | x10-5in/in/ °F | 7.0 | |
| Heat Deflection Temp | at 264 psi | ASTM D648 | °C(°F) | 75(167) |
| Thermal Conductivity | C177 C177 | x10-4cal/cm-sec- °C BTU-in/ft2-hr- °F | 3.44 1.0 | |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | – | °C(°F) | 177(305) | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | short time, 1/8″ thick | ASTM D149 | V/mil | 500 |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | – |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | – |
| Volume Resistivity | at 50% RH | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 1018 |
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone)
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone)

Chemicals which interact with PEEK polymer are not pH dependent; rather, interaction is more determined by other physical properties of the chemical(s) in question. Not recommended for use with nitric acid; sulfuric acid; halogenated acids, such as hydrofluoric, hydrobromic, and hydroiodic acids (hydrochloric acid is approved for most applications); and pure halogenated gases. Additionally, due to a swelling effect, be cautious in using the following solvents with PEEK tubing: methylene chloride, THF, and DMSO.
| Temperature Range | up to 100 °C (tubing); up to 125 °C (fittings) |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | 14cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation; ethylene oxide; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Relative Density | (Crystalline) (Amorphous) | ASTM D792 ASTM D792 | – – | 1.30 1.26 |
| Typical Level of Crystallinity | – | % | 30-35 | |
| Mold Shrinkage | – | % | 1.0-1.8 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. @ 73 °F Equilibrium @ 73 °F | ASTM D570 ISO R62A | % % | 0.50 0.50 |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | @ 73 °F (yield) @ 482 °F (yield) | ASTM D638 (5mm/min) ASTM D638 (5mm/min) | psi psi | 14,000 1,750 |
| Elongation at Break | @ 73 °F | ASTM D638 (5mm/min) | % | >50 |
| Elongation at Yield | @ 73 °F | ASTM D638 (5mm/min) | % | 4.9 |
| Flexural Modulus: | @ 73 °F @ 248 °F @ 482 °F | ASTM D790 ASTM D790 ASTM D790 | psi psi psi | 594,000 580,100 43,500 |
| Flexural Strength | @ 73 °F @ 248 °F @ 482 °F | ASTM D790 ASTM D790 ASTM D790 | psi psi psi | 24,650 14,500 1,800 |
| IZOD Impact Strength | @ 73 °F Notched Unnotched | ASTM D256 | ft.-lb./in. | 1.57 No Break |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Melting Point | DSC | °F (°C) | 644(340) | |
| Glass Transition Temperature, Tg (onset value) | DSC | °F (°C) | 289(143) | |
| Melt Flow Index | 400 °C/2.16 kg | ASTM D1238 | g/10 min. | 4 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: | <Tg >Tg | ASTM D696 ASTM D696 | 10-5 °F-1 | 2.6 6 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature, 264 psi | ASTM D648 | °F (°C) | 320(160) | |
| UL Continuous Use Temperature | Mechanical Electrical | 464(240) 500(260) | ||
| Sterilization | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| 200 steam cycles at 280 °F | short time, 1/8″ thick | – | – | No Effect |
| 1000 Mrads gamma radiation | – | – | No Effect | |
| Chemicals (ethylene oxide, etc.) | – | – | No Effect | |
| Heat up to 500 °F | – | – | No Effect | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength (50µ film) | ASTM D149 | KV/cm | 190 | |
| Dielectric Constant | 50Hz-10kHz, 0-300 °F 50Hz, 392 °F | – | 3.20-3.30 4.50 |
Perlast®
Perlast®

Perlast® Perfluoroelastomer is a special type of rubber material designed to offer the unique chemical resistance of PTFE. It shares with PTFE a polymer backbone consisting of carbon atoms protected by fluorine atoms, making it very inert to chemical attack. As a rubber, therefore, it is resilient, so it doesn’t creep or flow but retains sealing force over a long period. Perlast can be used in long-term conditions and has a very low oxygen permeability. It also stretches – aiding installation.
| Temperature Range | Maximum operating temp: +280 °C (+536 °F) Minimum operating temp: -35 °C (-31 °F) |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Et-0, Gamma irradiation, thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Perlast Extended Properties
| Physical Properties | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Hardness (points) | (=ISO 48) | ASTM D 1415 | °IRHD | 69 |
| Tensile Strength | (=ISO 37) | ASTM D 412 | MPa | 9.0 |
| Elongation at Break | (=ISO 37) | ASTM D 412 | % | 190 |
| 100% Modulus | (=ISO 37) | ASTM D 412 | MPa | 4.0 |
| Compression Set, Method B: | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| 24 hours at 200 °C (392 °F) | (=ISO 815) | ASTM D 395 | % | 21 |
| Heat Resistance: | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| 72 hours at 250 °C (482 °F) | (=ISO 188) | ASTM D 573 | ||
| Hardness change (points) | (=ISO 48) | ASTM D 1415 | °IRHD | -7 |
| Tensile strength change | (=ISO 37) | ASTM D 412 | % | 3.5 |
| Elongation at break change | (=ISO 37) | ASTM D 412 | % | +12 |
| Low Temperature Properties: | Test Method | Units | Typical Value | |
| TR10 | ASTM D 1329 | °C (°F) | -12 (-4) |
PFA
PFA

PFA is another good, general replacement for PTFE. PFA, while being more expensive than FEP, offers a higher maximum recommended use temperature for more demanding temperature applications. It is also offers less impurities for sensitive fluidics applications.
| Temperature Range | up to 80 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 881cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide, thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
PFA Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. | D570 | % | <0.03 |
| Weather and Chemical Resistance | – | – | outstanding | |
| Limiting Oxygen Index | D2863 | % | >93 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) 23 °C (73 °F)(yield) | D3307 D3307 D3307 | MPa(psi) MPa(psi) MPa(psi) | 25(3,600) 14(1,800) 13.8(2,000) |
| Ultimate Elongation | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) | D790 D790 | % % | 300 480 |
| Flexural Modulus | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) | D3307 D3307 | MPa(psi) MPa(psi) | 590(85,000) 55(8,000) |
| Specific Gravity | D792 | – | 2.12-2.17 | |
| Hardness Durometer | D2240 | – | D55 | |
| MIT Folding Endurance | 0.18-0.20mm(.007-.008 in.) | D2176 | Cycles | 15,000 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Nominal Melting Point | DTA-E168 | °C (°F) | 302-310 (575-590) | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 21-100 °C 70-212 °F 100-149 °C 212-300 °F 149-208 °C 300-408 °F | D696 D696 D696 D696 D696 D696 | mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F | 14×10-5 7.6×10-5 17×10-5 9.2×10-5 21×10-5 11.5×10-5 |
| Upper Service Temperature | – | °C (°F) | 260(500) | |
| Flow Rate | D3307 D3307 D3307 | g/10 min g/10 min g/10 min | 12-15(B) 15-18(A) 18-21(D) | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | Short time, 0.25 mm (0.10 in) | D149 | kV/mm (V/mil) | 80(2,000) |
| Dielectric Constant | 60 – 106 Hz | D150 | – | 2.03 |
| Dissipation Factor | 60 – 106 Hz | D150 | – | 0.0001 |
| Volume Resistivity | D-257 | ohm-cm | 1018 |
HPFA and HPFA+
HPFA and HPFA+
HPFA and HPFA+ differ from PFA simply in the amount of impurities left behind in the polymer matrix. Already one of the cleanest polymers on the market, PFA still had too many impurities for such industries as the medical and semiconductor industries. For these types of specialized needs, a higher purity form of PFA was developed. Differing only in the level of impurities, HPFA and HPFA+ offer all the same benefits of regular PFA.
| Temperature Range | up to 80 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 881cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation, thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
HPFA and HPFA+ Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. | D570 | % | <0.05 |
| Weather and Chemical Resistance | – | – | outstanding | |
| Limiting Oxygen Index | D2863 | % | >95 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) 23 °C (73 °F)(yield) | D3307 D3307 D3307 | MPa(psi) MPa(psi) MPa(psi) | 25(3,600) 14(1,800) 13.8(2,000) |
| Ultimate Elongation | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) | D3307 D3307 | % % | 300 480 |
| Flexural Modulus | 23 °C (73 °F) 250 °C (482 °F) | D790 D790 | MPa(psi) MPa(psi) | 590(85,000) 55(8,000) |
| Specific Gravity | D792 | – | 2.12-2.17 | |
| Hardness Durometer | D2240 | – | D55 | |
| MIT Folding Endurance | 0.18-0.20mm(.007-.008 in.) | D2176 | Cycles | 15,000 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Nominal Melting Point | DTA-E168 | °C (°F) | 302-310 (575-590) | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 21-100 °C 70-212 °F 100-149 °C 212-300 °F 149-208 °C 300-408 °F | D696 D696 D696 D696 D696 D696 | mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F mm/mm/ °C in./in./ °F | 14×10-5 7.6×10-5 17×10-5 9.2×10-5 21×10-5 11.5×10-5 |
| Upper Service Temperature | – | °F / °C | 260(500) | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | Short time, 0.25 mm (0.10 in) | D149 | kV/mm (V/mil) | 80(2,000) |
| Dielectric Constant | 60 – 106 Hz | D150 | – | 2.03 |
| Dissipation Factor | 60 – 106 Hz | D150 | – | 0.0001 |
| Volume Resistivity | D-257 | ohm.cm | 1018 |
PK (Polyketone)
PK (Polyketone)
PK: A proprietary polymer blend comprised mainly of polyetheretherketone (PEEK). PK demonstrates all of the superior chemical resistance of PEEK (see PEEK above). The proprietary blend will however, allow a fitting to attain
a higher pressures while reducing the cold flow properties of pure PEEK.
CAUTION: some fittings molded of PK are known to be conductive. Use caution when employing PK fittings in high voltage applications.
| Temperature Range | Temperature limit for PK is 200 °C, 392 °F |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation; ethylene oxide; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
PK (Polyketone) Extended Properties
| General | Test Method | Units | Typical Value | |
| Relative Density | ASTM D792 | – | 1.45 | |
| Mold Shrinkage | – | mil/in | 2-8 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | @ 73 °F (yield) | ASTM D638 | psi | 30,000 |
| Elongation at Yield | @ 73 °F | ASTM D638 (5mm/min) | % | 1.5 |
| Flexural Modulus: | @ 73 °F | ASTM D790 | psi | 2,300,000 |
| Flexural Strength | @ 73 °F | ASTM D790 | psi | 44,000 |
| IZOD Impact Strength | @ 73 °F Notched Unnotched | ASTM D256 | ft.-lb./in. | 1.2 11 |
| Thermal | Test Method | Units | Typical Value | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: | ASTM D696 | 10-5 °F– | 4 | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature, 264 psi | ASTM D648 | °F (°C) | 634(334) |
Polyethylene
Polyethylene
Polyethylene tubing has good chemical resistance. Take caution when using chlorinated solvents and some cyclic compounds.
| Temperature Range | up to 100 °C |
| Thread Strength | N/A |
| Oxygen Permeability | 500 cc-mil/100in_-24hr-atmcc-mil/100in_-24hr-atm |
| pH Range | 1-10 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Gamma irradiation, ethylene oxide |
| Autoclavable? | N |
Polyethylene Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 0.92 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min. | 6.6 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | % | 0.1 |
| Hardness, Shore D | ASTM D2240 | – | 54 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 610 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ASTM D638 | GPa(ksi) | 1.5(2.2) | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | GPa(ksi) | 35.3(51.2) | |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ATSM D790 | MPa(psi) | 11.8(1710) | |
| Izod Impact Strength | Notched, room temp. | ATSM D256 | ft-lb/in | 8.5 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C | µm/m- °C | 10.1 | |
| Deflection Temperature | at 0.46 MPa | ASTM D648 | °C(°F) | 45(316) |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Deflection Temp at 1.8 MPa | – | °C(°F) | 158(316) |
| Vicat Softening Temperature | ASTM D1525 | °C(°F) | 98(208) |
Polyoxymethylene (POM or Acetal)
Polyoxymethylene (POM or Acetal)

Polyoxymethylene (POM) has a wide variety of applications in industrial fields and often used in wet engineering environments. Characterized by high stiffness, low friction, and dimensional stability, POM is also known as acetal, polyacetal, or polyformaldehyde.
| Temperature Range | Up to 80°C |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils and most organic solvents |
| pH Range | 4 – 9 |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Polypropylene
Polypropylene

Polypropylene is used across many industries as a good, general-use polymer. It offers resistance to many standard chemical solutions across the full pH range, making it a product of choice for many applications. There are chemicals that will interact with polypropylene, either degrading it, discoloring it, or causing it to crack, and as such, it is important to ensure that the chemical solutions being used are compatible with this polymer. Such chemicals include chlorinated and aromatic solutions, as well as some organic solvents.
| Temperature Range | up to 40 °C |
| Thread Strength | Fair |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Polypropylene Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hours Sat. | ASTM D570 ASTM D570 | % % | 0.03 0.2 |
| Density | ASTM D792B | g/cc | 0.9 | |
| Melt Flow Rate | 230 °C/2.16kg | ASTM D1238 | g/10 min. | 11 |
| Haze | ASTM D1003A | % | 10 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 77 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 30(4,351) |
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | ASTM D790A | GPa(ksi) | 1(145 |
| Impact Strength | ASTM D256A | ft-lb/in | 1.2 | |
| Elongation | Yield | ATSM D638 | % | 13 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Heat Deflection Temp | at .46 MPa, °C | ASTM D648 | °F | 183 |
| Maximum Continuous Temperature | ASTM D794 | °F | 220 |
Polysulfone
Polysulfone

In general, polysulfone is chemically resistant and can be used in many applications. There are some chemicals, however, that should not be used. Primarily, chlorinated organic solutions should be avoided, as should some alcohols and some aromatic hydrocarbons.
| Temperature Range | up to 100 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | 230cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Polysulfone Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hours | ASTM D570 | % | 0.03 |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.24 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Yield | ASTM D638 | psi | 10,153 |
| Elongation | Break 50 – 100% Yield | ATSM D638 ATSM D638 | % % | 75 6 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | GPa | ASTM D638 | ksi | 360 |
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | ATSM D790 | ksi | 390 |
| Flexural Yield Strength | MPa | ATSM D790 | ksi | 15,374 |
| Impact Strength | Izod, J/cm Notched | ATSM D256 | ft-lb/in | 1.3 |
| Tensile Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | – | ft-lb/in2 | 200 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | 20 °C Tansvers to Flow, µm/m- °C | in flow; ASTM E381 ASTM E381 | µin/in- °F µin/in- °F | 31 31 |
| Deflection Temp | at 1.8 MPa, °C | ASTM D648 | °F | 345 |
| Maximum Continuous | Temperature | UL Relative Thermal Index, Electrical per UL 746B. Mechanical with impact 140 °C (280 °F); Mechanical without impact 160 °C(320 °F) | °F | 320 |
| UL RTI | Electrical, °C Mechanical with Impact, °C Mechanical without impact, °C | at 0.51mm at 0.51mm at 0.51mm | °F °F °F | 320 284 284 |
| Flammability UL94 | 5=V-0; 4=V-1; 3=V-2; 1=HB | HB @ 1.47mm | HB | 1 |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 5E+16 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1kHz Low Frequency, 1kHz | ASTM D150 ASTM D150 | – – | |
| Dielectric Strength | ASTM D149 | kV/in | 432 | |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1kHz Low Frequency, 1kHz | ASTM D150 ASTM D150 | kHz kHz | 0.0015 0.0015 |
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide)
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide)
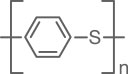
PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) is a highly chemical resistant polymer for room temperature and slightly elevated temperature applications. Great care should be taken, however, when using the polymer in elevated temperatures, as studies have shown the polymer to lose much of its chemical resistance properties when the temperature is too high. Additionally, the chemicals that show an effect with PPS are not pH dependent; however it is recommended to investigate specific compatibility prior to using strong acids or bases and some halogenated organic solutions.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.70 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour immersion | – | % | 0.02 |
| Moisture Absorption at Equilibrium | Saturated immersion | – | % | 0.02 |
| Hardness, Rockwell M | ASTM D785 | – | 94 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 125 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell D | ASTM D2240 | – | 86 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 90(13,053) |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 2 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | GPa | ASTM D638 | 725 ksi | 5 |
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | ASTM D790 | 1000 ksi | 6.9 |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 165(23,061) | |
| IZOD Impact Strength | J/cm | ASTM D256 Type A | 0.99 ft.-lb./in. | 0.53 |
| Compressive Yield Strength | ASTM D256 10% Def | MPa(psi) | 165(23,061) | |
| Compressive Modulus | GPa | ASTM D695 | 1,305 ksi | 9 |
| K (wear) Factor | 10-10 in3-min/lb-ft-hr | PTM55010 | – | 999 |
| Limiting Pressure Velocity | MPa-m/sec | PTM55010 | 3,426 psi-ft/min | 0.12 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C, µm/m- °C | ASTM E837 (TMA) | 25 µin/in- °F | 45 |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8 MPa, °C | ASTM D648 | 489 °F | 254 |
| Melting Point °C | ASTM D3418 | 540 °F | 282 | |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Air, °C | Contiuous Service without load | 450 °F | 232 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m-K | – | 2.1 BTU-in/hr-ft2– °F | 0.3 |
| Flammability, UL94 | (5=V-0; 4=V-1; 3=V-2; 1=HB | V-0 UL 94 | 5 | 5(V-0) |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | Lower Limit | ASTM D257 | 1E+15 ohm-cm | 5(V-0) |
| Dielectric Strength | Short Term | ASTM D149(2) | 386 kV/in | 15.2 |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer formed by polymerization of vinyl chloride. It has a high hardness, mechanical and insulative properties with high corrosion and chemical resistance. It is highly machinable allowing close tolerances and versatile in medical and industrial applications.
| Temperature Range | Up to 50°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Not resistant to aromatic hydrocarbons |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Autoclavable? | N |
Radel® R
Radel® R Extended Properties

Radel® R (polyphenylsulfone) tubing offers very high burst pressure and good chemical compatibility. This amorphous polymer can withstand repeated autoclave sterilization cycles because of its excellent thermal properties. Our Radel tubing is transparent, making visual monitoring of flow possible in high-pressure tubing. Chemicals that react with Radel are not pH dependent, please consult the chemical compatibility section of the website for more information on specific chemicals.
| Temperature Range | up to 100 °C |
| Thread Strength | N/A |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 1 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Thermal, gamma irradiation |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Radel R Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.29 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min | 11.5 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | % | 0.37 |
| Water Absorption at Saturation | Immersion | ASTM D570/ ISO 62 | % | 1.10 |
| Hardness, Rockwell M | ASTM D785 | – | 80 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 120 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 70(10,100) |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 60-120 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ASTM D638 | GPa(ksi) | 2.4(345) | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | GPa(ksi) | 2.4(350) | |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 106(15,500) | |
| Izod Impact Strength | ASTM D256 | J/cm(ft-lb/in) | 6.9(13) | |
| Unnotched | ASTM D256 | No break | ||
| Tensile Impact Strength | ASTM D1822 | kJ/m2(ft-lb/in2) | 400(190) | |
| Compressive Yield Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 92(13,400) | |
| Shear Strength | ASTM D732 | MPa(psi) | 62(9,000) | |
| Poissons Ratio | – | 0.42 | ||
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C | ppm- °C (ppm- °F) | 56(31) | |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8 MPa | ASTM D648 | °C(°F) | 207(405) |
| Melting Point | ASTM D3418 | °C(°F) | 345-400(650-750) | |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Deflection Temp at 1.8 MPa | – | °C(°F) | 150(300) |
| Thermal Conductivity | – | BTU-in/hr-ft2- °F | 2.4 | |
| Flammability Rating, UL94 | (5=V-0;4=V-1;3=V-2;1=HB) | UL94 | mm(in) | 0.75(0.030) |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 1E+15 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 60 Hz | ASTM D150 | – | 3.4 |
| Dielectric Strength, kV/mm | 3.2 mm (0.125 in); Short Time | ASTM D149 | V/mil | 360 |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 0.002 |
ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene)
ETFE (Ethylene TetrafluoroEthylene) Extended Properties

ETFE is a molecular relative of PTFE, and as such, is highly chemically resistant. It has proven to be an excellent material for sealing surfaces and for applications where aggressive solvents are being used and durable tubing is necessary for the application. ETFE is also used for threaded products, particularly in our low pressure line of products and adapters. Please note that caution must be taken when using some chlorinated solvents with ETFE, as they may interact and degrade or swell the polymer slightly.
| Temperature Range | up to 80 °C |
| Thread Strength | Good |
| Oxygen Permeability | 100cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Ethylene oxide |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
ETFE (Ethylene TetrafluoroEthylene) Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. | ASTM D570 | % | 0.007 |
| Weather and Chemical Resistance | – | – | Excellent | |
| Limiting Oxygen Index | ASTM D2863 | % | 30-32 | |
| Bulk Density | DuPont | g/L | 1,300 | |
| Flame Rating | UL 94 | – | V-0 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 40(6,000) |
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D792 | – | 1.7 | |
| Ultimate Elongation | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D638 | % | 300 |
| Flexural Modulus | 23 °C (73 °F) | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 1,000(145,000) |
| Impact Strength | 23 °C(73 °F) | ASTM D256 | J/m(ft-lb/in) | No Break |
| Compressive Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 38(5,500) | |
| Linear Coefficient of Expansion | 0-100 °C 32-212 °F | ASTM D696 ASTM D696 | mm/mm/ °C in/in/ °F | 12.6 x 10-5 7.0 x 10-5 |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Nominal Melting Point | ASTM D3418 | °C (°F) | 255-280(491-536) | |
| Flow Rate | ASTM D3159 | g/10 min | 11 | |
| Upper Service Temperature | UL746 | °C (°F) | 155(311) | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | 0.25 mm (0.010 in) | ASTM D149 | kV/mm (V/0.001mil) | 70(1,800) |
| Dielectric Constant | 1 MHz, 23 °C(73 °F) | ASTM D1531 | – | 2.5-2.6 |
| Dissipation Factor | 1 MHz, 23 °C(73 °F) | ASTM D1531 | – | 0.0054 |
| Volume Resistivity | ASTM D257 | Tohm-m (ohm-cm) | 1×103 (1×1017) |
Titanium
Titanium
Titanium products were created initially as a biocompatible alternative to stainless steel — something that did not have ferrous components. While being a metal and therefore offering a higher temperature rating than polymers can offer, titanium does not exhibit the same strong chemical resistance that stainless steel does, and is particularly susceptible to attack by strong acidic or basic solutions. There are many other solvents that will interact with titanium, so it is recommended that a chemical compatibility chart be consulted.
| Temperature Range | up to 250 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 1 – 12 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation; ethylene oxide; thermal |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Titanium Extended Properties
| Titanium: Grade 2 / Condition: Annealed | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Mechanical – Meets ASTM F67 | |||
| Tensile Strength | – | Mpa(ksi) | 345(50) |
| Yield Strength | – | Mpa(ksi) | 275(40) |
| Elongation min (la) | – | 20 | |
| Composition – Meets ASTM F67 | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Carbon | – | 0.10 | |
| Nitrogen | 0.03 | ||
| Hydrogen | – | 0.0125 | |
| Iron | – | 0.3 | |
| oxygen | 0.25 | ||
| Titanium | – | Balance | |
TPX® (Polymethylpentene)
TPX® (polymethylpentene)

TPX® (polymethylpentene) is used sparingly in the Upchurch Scientific product line. It offers good chemical compatibility across the full pH range. However, it is suspect to attack by halogenated chemicals and a number of organic solutions as well. Additionally, research has shown that, as the operating temperature reaches and exceeds 60 °C, the resistance to chemical attack is lowered considerably.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | 206cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
TPX Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.28 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min | 9 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | % | 0.25 |
| Mold Shrinkage | % | 0.5 | ||
| Water Absorption at Saturation | Immersion | ASTM D570/ ISO 62 | % | 1.25 |
| Hardness, Rockwell M | ASTM D785 | – | 112 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 125 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 105(15,228) |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 80 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ASTM D638 | GPa(ksi) | 2.9(420) | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | GPa(ksi) | 3.3(479) | |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 150(21,700) | |
| Izod Impact Strength | Notched, at 23 °C | ASTM D256 | J/cm | 0.53 |
| Izod Impact Strength | Unnotched, at 23 °C | ASTM D256 | J/cm | 1.34 |
| Compressive Yield Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 151(22,000) | |
| Shear Strength | ASTM D732 | MPa(psi) | 103(15,000) | |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, 1E+6 cycles | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Poissons Ratio | – | 0.35 | ||
| Coefficient of Friction | Dynamic vs. carbon steel, 50mm/s (2in/s) | 0.42 | ||
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C | µin/in- °F | 31 | |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8 MPa | ASTM D648 | °F(°C) | 392(200) |
| Melting Point | ASTM D3418 | °F(°C) | 639-798 (337-426) | |
| Thermal Conductivity | – | BTU-in/hr-ft2- °F (W/m-K) | 0.90(0.22) | |
| Flammability Rating, UL94 | (5=V-0;4=V-1;3=V-2;1=HB) | UL94 | B | 1(HB) |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 1E+15 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 3.7 |
| Dielectric Strength, kV/mm | 2.3mm (90 mils); Short Time | ASTM D149 | 500 kV/in | 19.7 |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 0.005 |
| Arc Resistance | ASTM D495 | sec | 220 |
UHMWPE (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene)
UHMWPE (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene)

UHMWPE (ultra high molecular weight polyethylene) is a commonly-used polymer which offers resistance to many chemical solutions, particularly aqueous-based ones. The polymer is durable and ideal for use in many “room temperature” applications. Care should be taken when using anything that is manufactured from UHMWPE in conjunction with some organic solutions as well as chlorinated solvents and nitric acid.
| Temperature Range | up to 50 °C |
| Thread Strength | N/A |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 0 – 14 |
| Sterilization Techniques | |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
UHMWPE (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | 24 hr. | D570 | % | 0.001 |
| Density | lb/in3 (g/cm3) | D792 | – | 0.034 (0.93) |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | D638 | psi | 3,100 | |
| Tensile Modulus | D638 | psi | 125,000 | |
| Flexural Modulus | D790 | psi | 125,000 | |
| Compressive Strength | D695 | psi | 2,000 | |
| Hardness | Shore D | D785 | – | D62-D66 |
| IZOD | Notched Impact | D256 | ft-lb/in | No Break |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | D696 | 105 in/in/ °F | 11.1 | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | at 66psi | D648 | °C (°F) | 95(203) |
| Max operating Temperature | – | °C (°F) | 82(180) | |
| Thermal Conductivity | x10-4cal/cm-sec- °C BTU-in/ft2-hr- °F | C177 C177 | °C °F | 10.06 2.92 |
| Flammability Rating | UL94 | – | H-B | |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Dielectric Strength | (V/mil) | D149 | – | 900 |
| Dielectric Constant | at 50 KHz | D150 | – | 2.3 |
| Dissipation Factor | at 50 KHz | D150 | – | 0.0002 |
| Volume Resistivity | (ohm-cm) at 50% RH | D257 | – | >5 x 1016 |
Ultem®
Ultem®

Ultem® (polyetherimide) is an amorphous polymer with a high temperature resistance and excellent chemical compatibility. Upchurch Scientific extrudes tubing from this material, that is transparent and exhibits good kind resistance. Ultem meets the requirements for ISO10993, FDA and USP Class VI certification.
| Temperature Range | up to 125 °C |
| Thread Strength | N/A |
| Oxygen Permeability | 37 cc / 100in2 * 24h * atm / mil @ 25 °C |
| pH Range | 1 – 10 |
| Sterilization Techniques | Gamma radiation, ethylene oxide, dry heat |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Ultem Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Density | ASTM D792 | g/cc | 1.28 | |
| Melt Flow | 1.05kg/190 °C | g/10 min | 9 | |
| Water Absorption | 24 hour | ASTM D570 | % | 0.25 |
| Mold Shrinkage | % | 0.5 | ||
| Water Absorption at Saturation | Immersion | ASTM D570/ ISO 62 | % | 1.25 |
| Hardness, Rockwell M | ASTM D785 | – | 112 | |
| Hardness, Rockwell R | ASTM D785 | – | 125 | |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ASTM D638 | MPa(psi) | 105(15,228) |
| Elongation | Break | ASTM D638 | % | 80 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | ASTM D638 | GPa(ksi) | 2.9(420) | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D790 | GPa(ksi) | 3.3(479) | |
| Flexural Yield Strength | ASTM D790 | MPa(psi) | 150(21,700) | |
| Izod Impact Strength | Notched, at 23 °C | ASTM D256 | J/cm | 0.53 |
| Izod Impact Strength | Unnotched, at 23 °C | ASTM D256 | J/cm | 1.34 |
| Compressive Yield Strength | ASTM D695 | MPa(psi) | 151(22,000) | |
| Shear Strength | ASTM D732 | MPa(psi) | 103(15,000) | |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Fatigue Strength | Flexural fatigue endurance limit, 50% RH, 1E+6 cycles | ASTM D672 | MPa(psi) | 32(4,641) |
| Poissons Ratio | – | 0.35 | ||
| Coefficient of Friction | Dynamic vs. carbon steel, 50mm/s (2in/s) | 0.42 | ||
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | linear 20 °C | µin/in- °F | 31 | |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8 MPa | ASTM D648 | °F(°C) | 392(200) |
| Melting Point | ASTM D3418 | °F(°C) | 639-798 (337-426) | |
| Thermal Conductivity | – | BTU-in/hr-ft2- °F (W/m-K) | 0.90(0.22) | |
| Flammability Rating, UL94 | (5=V-0;4=V-1;3=V-2;1=HB) | UL94 | B | 1(HB) |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | ASTM D257 | ohm-cm | 1E+15 | |
| Dielectric Constant | at 1MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 3.7 |
| Dielectric Strength, kV/mm | 2.3mm (90 mils); Short Time | ASTM D149 | 500 kV/in | 19.7 |
| Dissipation Factor | at 1 MHz | ASTM D150 | – | 0.005 |
| Arc Resistance | ASTM D495 | sec | 220 |
Vespel®
Vespel®

Vespel® is a frequently-used polyimide material, often found in use with valves. While often adequate for use in systems where the chemicals do not go out of the pH range of 1 to 10, Vespel is susceptible to alkaline attack. This means that ammonia, hydrazines, amines, and any solution that surpasses pH 10 should be avoided. Also, strong oxidizing agents should be avoided or at least used with caution.
| Temperature Range | up to 200 °C |
| Thread Strength | Excellent |
| Oxygen Permeability | N/A |
| pH Range | 1 – 10 |
| Sterilization Techniques | gamma irradiation |
| Autoclavable? | Y |
Vespel Extended Properties
| General | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Water Absorption | for 24 hr. immersion | ISO 62 | % | 24 |
| Density | ISO 1183 | g/cc | 1.43 | |
| Mositure Absorption | at Equilibrium | 50% RH | % | 1.2 |
| Hardness | Rockwell M | ISO 2039-2 | – | 100 |
| Mechanical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Tensile Strength | Ultimate | ISO 527 | MPa(psi) | 86(12,473) |
| Elongation % | Break | ISO 527 | % | 75 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | GPa | ISO 527 in Tension | ksi | 319 |
| Impact Strength | Charpy, J/cm2 | ISO 179/1eA | ft-lb/in2 | 1.7 |
| Impact | Unnotched Charpy, J/cm2 | No break per ISO 179, 1eU | ft-lb/in2 | 4,755 |
| Compressive Yield Strength | at 1%; ISO 604 | psi | 3,336 | |
| Thermal | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 20 °C, µm/m- °C 100 °C, µm/m- °C | avg value between 23 & 100 °C avg value between 23 & 150 °C | µin/in- °F µin/in- °F | 25 25 |
| Deflection Temperature | at 1.8MPa, °C | ISO 75 method A | °F | 680 |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Air, °C 450 °C for short periods 240 °C for 20,000 hours continuous | – – – | – °F °F | – 842 842 |
| Thermal Conductivity | BTU-in/ft2-hr- °F | – | °F | 2.4 |
| oxygen Index | ISO 4589 | % | 53 | |
| Flammability Rating, UL94 | 5=V-0;4=V-1;3=V-2;1=HB | at 1.5 & at 3mm thickness | V-0 | 5 |
| Electrical | Condition | Test Method | Units | Typical Value |
| Electrical Resistivity | IEC 93 | ohm-cm | 1E+61 | |
| Surface Resistance | IEC 93 | ohm | 1E+15 | |
| Dielectric Constant | 1 MHz Low Frequency, 100 Hz | IEC 250 IEC 250 | – – | 3.6 3.6 |
| Dielectric Strength | kV/mm | IEC 243 | kV/in | 711 |
| Dissipation Factor | 1 MHz Low Frequency, 100 Hz | IEC 250 IEC 250 | – – | 0.003 0.002 |

